Manual finance—spreadsheets, swivel-chair data entry, reconciliations done at month-end—creates delays, errors, and audit risk. As organizations grow, these manual steps become bottlenecks that slow decision-making and obscure cash flow. Financial automation software changes the operating rhythm.
Instead of rekeying data and chasing exceptions, your team works from live information, with routine tasks handled by rules and AI. The result is faster closes, better compliance, stronger cash control, and more time for strategic analysis. In 2025, the bar is higher than ever: AI is now embedded in ERP suites, regulators move quickly, and CFOs are expected to lead cross-functional transformation—not just report on it.
Leading firms have already moved from “manual + spreadsheets” to “automated + continuous close,” using controls, workflows, and AI assistive features to reduce effort and improve visibility. Deloitte describes this shift toward a near-touchless close that improves accuracy, compliance, and efficiency—freeing finance to focus on higher-value work.
What is financial automation software?
Financial automation software automates, orchestrates, and monitors core finance processes: accounts payable (AP), accounts receivable (AR), bank reconciliation, payroll, expense management, and financial reporting. It differs from basic accounting tools by emphasizing end-to-end workflows (e.g., ingest invoice → extract → approve → post → pay), policy enforcement (e.g., controls, segregation of duties), and data unification across systems (ERP, CRM, payroll, banking). The goal isn’t only faster processing—it’s better decisions through real-time visibility and consistent data.
Research underscores the scale of the opportunity: McKinsey estimates that 42% of finance activities are fully automatable with existing tech and a further 19% mostly automatable, rebalancing finance time from transaction processing to analysis and planning.
Look no further to automate your finance processes
Our team will be happy to speak with you and guide you on the implementation of Microsoft Business Central.
 Free discovery call
Free discovery call
Why your business needs financial automation software?
Efficiency gains. Automation shortens record-to-report cycle times and reduces manual touchpoints. Firms implementing continuous close practices report fewer end-of-period spikes and better daily cash and variance visibility.
Lower error rates. Eliminate rekeying and manual reconciliations; auto-matching and rules catch mismatches early. McKinsey case work shows large institutions automating 60–70% of record-to-report tasks with 30%+ efficiency gains—and some processes achieving 80% cost reduction.
Compliance and auditability. Automated audit trails, approvals, and standardized reporting make external audits and internal reviews faster and less disruptive—aligning with governance expectations for modern close, consolidation, and reporting solutions.
Strategic finance & talent retention. As automation expands, top-quartile finance functions spend more time generating insights than performing automatable tasks, shifting the team’s role toward business partnership.

Levels of financial automation maturity
Basic (task automation). Standalone accounting tools (e.g., AP/AR automation, invoice capture, bank feeds) handle narrow tasks. Value: fewer manual steps and faster processing—but data still lives in silos.
Intermediate (connected finance). Finance workflows are integrated across AP/AR, bank feeds, and reporting, often tied into CRM/HR. Value: one source of truth and shorter close cycles.
Advanced (ERP + AI). End-to-end automation across finance and operations in an ERP with embedded Copilot/AI for summarization, anomaly detection, and forecast assistance. In Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central, for example, Copilot skills assist with bank reconciliation and automate repetitive tasks; Microsoft also provides Copilot for Finance that connects to Business Central for collections and related workflows in Outlook.
How much can you save with Business Central?
Download your free ROI Excel calculator to discover how much savings you can make by implementing Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central today.

Key finance processes you can automate
Accounts Payable (AP). Ingest invoices (PDF/email/EDI), extract data, validate, route for approval, and schedule payment; lower processing cost and shrink cycle times with exception-based review. Analyst research on close and consolidation software highlights automation’s role in reducing process costs and improving control.
Accounts Receivable (AR). Generate invoices, sync payment options, trigger dunning workflows, and reconcile receipts. Well-run AR automation improves DSO and cash-flow predictability (and increasingly integrates with email assistants for collections).
Reconciliation. Auto-matching bank transactions to ledger entries, surfacing only exceptions. In Business Central, bank reconciliation assist helps users resolve unmatched lines faster.
Payroll & expenses. Policy enforcement, tax compliance, and paperless reimbursement reduce back-office load and risk. (Popular SMB suites document how automation simplifies payroll calculations, filings, and reporting.)
Reporting & analytics. Live dashboards, drill-downs, and AI-supported analysis (e.g., Business Central’s Analysis Assist and Copilot features) shift reporting from static PDFs to real-time decision support.

Types of financial automation software
Off-the-shelf (accounting-first). Tools like Xero and QuickBooks are easy to adopt, strong for SMB bookkeeping and basic automation (bank feeds, recurring invoices, payroll), but can hit integration or consolidation limits at scale.
ERP-integrated (finance-plus-operations). Suites like Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central connect finance to sales, supply chain, and inventory, with AI and workflow spanning departments. Best for mid-market or multi-entity teams seeking end-to-end control.
Custom/low-code platforms. Low-code tools (e.g., SolveXia) help finance build tailored automations, especially for heavy reconciliation, data prep, and bespoke reporting—while relying on strong governance.
Talk to an ERP finance specialist today
Contact us for more details on our services and discover why Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central is the leading financial automation software.
 Free discovery call
Free discovery call
Financial automation for SMBs vs enterprises
SMBs prioritize time-to-value, simplicity, and predictable costs. Typical wins: digitizing AP, auto-reconciling bank feeds, and standardizing invoicing. Off-the-shelf tools or Business Central configured for a single entity can deliver meaningful gains without heavy IT lift.
Enterprises emphasize scale, internal controls, consolidation, and regulatory agility across multi-entity, multi-currency environments. Gartner frames this category as Financial Close and Consolidation Solutions (FCCS)—supporting close, consolidation, and reporting with automation and controls across the group.
Outcome focus differs: SMBs often measure hours saved per month and fewer errors; enterprises measure DSO improvements, close cycle reductions, and audit readiness across regions. McKinsey cases show large finance functions realizing 30%+ run-rate efficiencies after automating record-to-report at scale.
Top financial automation software examples for 2025
1. Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central (ERP-integrated automation)

A cloud ERP for SMBs and mid-market organizations that unifies finance with sales, supply chain, and operations. Business Central embeds Copilot skills (e.g., chat, analysis assist, and bank reconciliation assist) and supports integration with Copilot for Finance inside Microsoft 365 apps like Outlook for collections. These assistive and agent-style capabilities aim to reduce repetitive work and make close tasks “near-touchless.”
You get end-to-end workflows—posting groups, approvals, dimensions—and native analytics with Power BI and Microsoft 365. Microsoft’s 2025 wave plans continue to expand Copilot and autonomous agents for core scenarios, signaling a steady cadence of AI features. For organizations standardizing on Microsoft 365, the ecosystem advantage is significant.
A Forrester Total Economic Impact (TEI) study of organizations migrating from on-prem Microsoft ERP to Business Central reported 265% ROI over three years and $529K NPV for a 150-employee composite, underscoring strong value for SMB/mid-market transitions to cloud ERP.
2. Stripe (revenue + finance automation for billing, tax & recognition)

Stripe’s Revenue & Finance Automation suite spans Billing (recurring/usage-based, tiered pricing, customer portal, dunning & smart retries), Revenue Recognition (IFRS 15/ASC 606 accrual automation, revenue waterfalls, API access), and Revenue Recovery features to reduce failed payments and churn. This stack pairs naturally with product-led and SaaS models.
Stripe focuses on monetization speed and developer ergonomics: pricing model flexibility (flat, per-seat, usage-based), fast go-lives via hosted components, and deep data for finance reporting. The company’s Billing product was named a Leader in Forrester’s Recurring Billing Solutions, Q1 2025—a useful external signal for teams comparing vendors.
High-growth digital businesses that need global payments, agile pricing, automated revenue schedules, and finance-grade reporting without stitching together multiple point solutions.
3. BlackLine (financial close, account reconciliation, and controls)

BlackLine is a specialist platform for financial close and account reconciliation—centralizing reconciliations, tasks, journals, and controls in a single cloud environment. Its architecture targets period-end control, variance analysis, and audit readiness with dashboards for controllers and CFOs.
Rather than being a general ledger or planning tool, BlackLine is built for the “last mile” of finance—matching, certifying, and documenting accuracy. Organizations adopt it to standardize reconciliations, reduce manual journals, and gain a governed path to continuous close. Gartner’s Peer Insights site highlights this category’s purpose and provides third-party user reviews for due diligence.
Mid-to-large organizations seeking to modernize close with strong control frameworks and audit trails, often alongside an ERP—especially when multi-entity consolidation and detailed reconciliation are critical.
4. Xero (SMB accounting with useful automation)

Xero is a cloud accounting platform popular with small businesses and accountants. Standout automations include bank feeds, bank rules, recurring invoices, and automatic invoice reminders—plus a growing ecosystem of integrations (payments, payroll, expenses).
For SMBs that need straightforward bookkeeping with helpful automation (and limited IT overhead), Xero’s UX, add-ons, and accountant familiarity shorten the learning curve. The product’s invoicing automation can nudge late payers and reduce manual follow-ups, and bank feeds reduce data entry by pulling transactions automatically.
Smaller finance teams prioritizing speed of setup and everyday automation over advanced consolidation or complex multi-entity needs.
5. QuickBooks (SMB accounting with payroll and invoicing automation)

QuickBooks remains a staple for small businesses, combining accounting with automated invoicing, payment matching, and payroll automation (calculations, filings, reports). Guides and product documentation emphasize how automation reduces manual steps and helps owners stay compliant without a dedicated finance staff.
QuickBooks offers multiple payroll tiers and an accessible UI, with automation spanning tax withholdings, time tracking, and direct deposit, helping teams avoid errors typical of manual payroll. Feature comparison pages make it easier to right-size plans as a business grows.
SMBs and sole proprietors looking for all-in-one basics—invoices, payments, payroll—without jumping to ERP. (It can also serve as a stepping stone to ERP when multi-entity or advanced controls are required later.)
6. SolveXia (no-code finance automation for reconciliations & reporting)

SolveXia is a no-code platform tailored to finance: data preparation, reconciliations, workflow orchestration, and reporting. It connects to ERPs and other systems, empowering finance teams to design and run their own automated processes (e.g., complex reconciliations, revenue and expense analysis, rebate/chargeback calculations) on the Microsoft Azure cloud.
Flexibility. Teams can replace multi-worksheet spreadsheets, reduce copy-paste risk, and standardize hand-offs with governed workflows. Review sites describe it as a strong fit for data-heavy processes where finance wants control without heavy coding.
Mid-market and enterprise finance groups that need tailored automations and granular reconciliations alongside (not instead of) their ERP.
How to choose the best financial automation software?
Start with outcomes. Is your primary constraint invoice throughput, error rates, time-to-close, or compliance? Rank the problems to solve in the next 6–12 months.
Map to maturity. If you’re early, consider SMB-friendly tools (Xero/QuickBooks) or a scoped Business Central deployment; if you’re handling multi-entity consolidations or need embedded controls, aim for ERP-level automation and/or close solutions.
Check the stack. Integrations to ERP/CRM/HR and banking are non-negotiable. Evaluate AI features (forecasting, anomaly detection, reconciliation assist) and roadmap cadence—Microsoft’s public release plans for Business Central, for instance, show continued Copilot and agent investments.
Validate with proof. Look for third-party studies and peer reviews. For Business Central, Forrester’s TEI provides quantified ROI; for billing, Forrester’s Wave offers comparative analysis of vendors including Stripe.
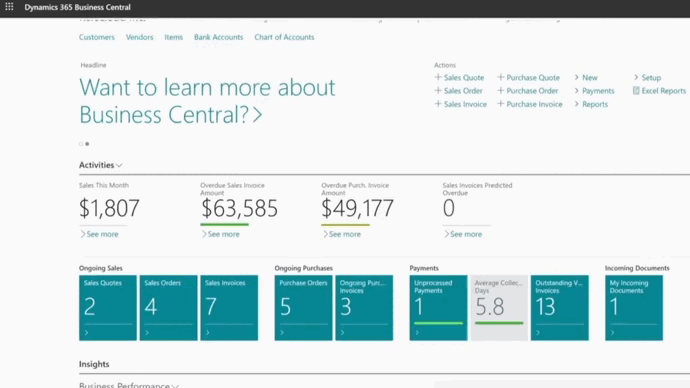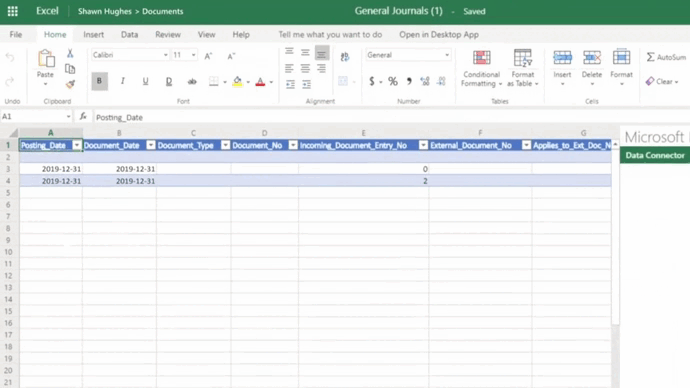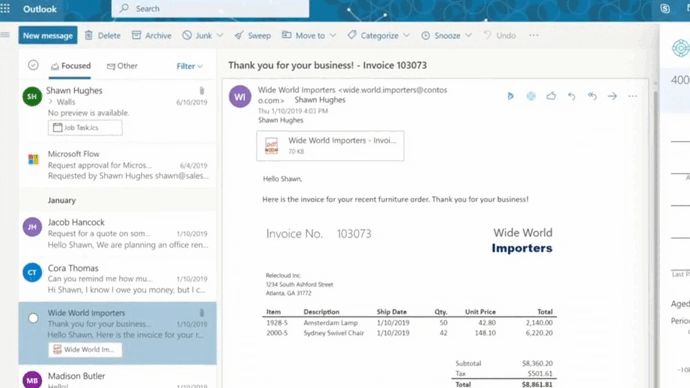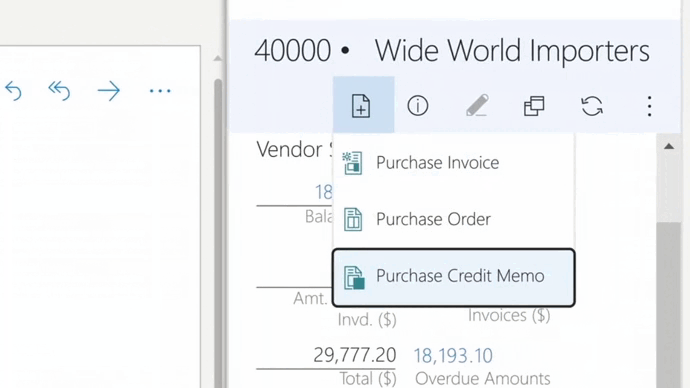
The ROI of financial automation software
Hard savings and soft gains. Automation reduces labor time in AP/AR, journal entries, and reconciliations; shrinks error remediation; and avoids legacy infrastructure costs. McKinsey documents 30%+ run-rate efficiencies in record-to-report with scaled automation, and some processes see 80% processing-cost reductions.
Continuous close → faster insights. Deloitte finds that moving to a near-touchless close improves accuracy and frees finance to focus on value-added analysis, which drives better decisions and governance.
Third-party validation. For organizations migrating from on-prem Microsoft ERP to Dynamics 365 Business Central, Forrester’s TEI reports 265% ROI over three years and $529K NPV for a 150-employee composite—capturing benefits across finance, operations, and sales users.
Revenue operations ROI. On the revenue side, modern billing stacks like Stripe Billing support usage-based/tiered pricing, revenue recovery features, and automated revenue recognition to accelerate cash and reduce leakage—capabilities recognized in Forrester’s Wave for Recurring Billing Solutions (Q1 2025).
Challenges and risks of financial automation (and how to manage them)
Misconfiguration risk. Poorly designed workflows can mispost transactions or misapply recognition rules. Mitigation: segregated responsibilities, testing environments, and staged rollouts.
Data integration & quality. Legacy systems and inconsistent master data are the top blockers. Mitigation: prioritize data governance, define owners, and standardize chart of accounts and dimensions before turning on automation.
Change management. Employees worry about job loss or tool fatigue. Mitigation: communicate “automation augments people,” retrain roles toward analysis and business partnering (a trend supported by PwC’s benchmarking).
Cybersecurity & compliance. Finance handles sensitive data; choose platforms with compliance attestations and strong access controls. For close/consolidation, consult the FCCS category guidance and evaluate vendors with peer reviews for control depth.
Book your free consultation today
Contact us for more details about financial automation software and how Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central fits the bill.
 Free discovery call
Free discovery call
Future of financial automation software
AI copilots and agents. Expect copilots to expand from assistance (summaries, Q&A, recon help) into autonomous agents that watch thresholds and propose entries or route exceptions—already visible in Microsoft’s release plans.
Proactive finance. Systems will flag anomalies, forecast cash, and recommend corrective actions, turning finance into a real-time advisory function.
Ecosystem convergence. Billing, payments, revenue recognition, and tax continue consolidating into unified revenue stacks; on the back end, ERP and close tools trend toward continuous consolidation and disclosure orchestration. Analyst conferences and MQ/Wave research reflect this convergence.
Talent model shift. With more tasks automated, finance roles skew toward analytics, scenario design, and business partnering—a shift already observed in top-quartile functions.
Why Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central is a strong choice?
Business Central gives SMBs and midsize enterprises ERP-level financial automation without the overhead of legacy on-prem systems. You get posting groups, approvals, dimensions, intercompany, consolidation, and Copilot-powered help for analysis and reconciliation—plus the option to surface Business Central data within Microsoft 365 Copilot for Finance to streamline collections in Outlook. The public release plans highlight continued Copilot and autonomous agents investment.
On ROI, Forrester’s TEI provides rare third-party quantification: 265% ROI over three years and $529K NPV for a cloud migration to Business Central—making the business case clear for organizations ready to retire fragmented, manual processes.
Financial automation software isn’t just about “getting the books done faster.” It’s about operating differently—with live data, strong controls, and AI-assisted workflows that turn finance into a continuous, insight-ready function. The benefits are tangible: shorter closes, fewer errors, better compliance, and proven ROI. Whether you start with billing automation on the revenue side or drive an ERP-led transformation with Business Central, the path is clear—and the competitive advantages compound.
Ready to modernize your finance stack? Gestisoft can help you select the right approach and implement Business Central to deliver fast wins and durable ROI.
-
Software that automates finance tasks (AP, AR, reconciliations, payroll, reporting) with workflows, controls, and integrations—often embedded in ERP suites with AI assistance. McKinsey estimates 42% of finance activities fully automatable today and another 19% mostly automatable.
Liked what you just read? Sharing is caring.

August 22, 2025 by Kooldeep Sahye by Kooldeep Sahye Marketing Specialist
Fuelled by a passion for everything that has to do with search engine optimization, keywords and optimization of content. And an avid copywriter who thrives on storytelling and impactful content.
