Choosing the right types of ERP software is one of the most important technology decisions a business can make. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) has moved beyond being just a finance or accounting tool—it’s now the backbone of digital transformation, connecting finance, operations, HR, supply chain, and customer management into a single platform.
But with so many ERP software types available—on-premise, cloud, hybrid, industry-specific, and modular—it can be difficult for organizations to know which path to take. This guide walks you through everything you need to know about the different types of ERP software, their benefits, challenges, and how to choose the right solution for your business.
What is ERP software?
ERP software (Enterprise Resource Planning software) is a business management platform that centralizes data and automates processes across core business functions. Instead of running multiple disconnected applications for finance, inventory, sales, and HR, ERP systems integrate them into one unified database.
The first versions of ERP evolved from Material Requirements Planning (MRP) systems in the 1960s and 1970s. These early tools focused on manufacturing schedules and inventory control. Today, ERP solutions go much further: they manage finances, HR, supply chains, customer data, and analytics across industries of every size.
Modern ERP software is modular, cloud-ready, and often enhanced with artificial intelligence (AI) and real-time analytics, giving companies the agility they need to compete in a fast-changing market.
Learn more about our ERP solution now
Contact us for a free consultation with our team of experts.
 Free discovery call
Free discovery call
Why understanding the different types of ERP software matters?
Selecting the wrong ERP system can be costly. Implementation failures often result from businesses not fully understanding the different types of ERP software and how each fits specific needs.
For example:
- A small business might overspend on a highly customized on-premise system when a cloud ERP would be more scalable and affordable.
- A manufacturing company might miss critical features if it selects a generic ERP system rather than one designed for production processes.
- Organizations with strict compliance rules may need a hybrid ERP model to balance data security with flexibility.
Understanding the options ensures that you:
- Maximize ROI by choosing the right fit.
- Avoid hidden costs like extensive customizations or complex migrations.
- Support your long-term growth strategy instead of locking into short-term fixes.

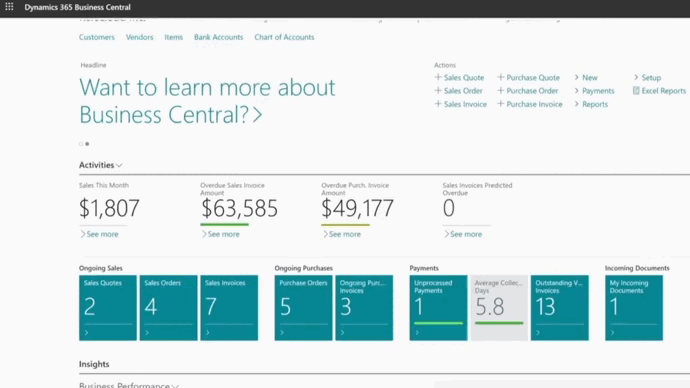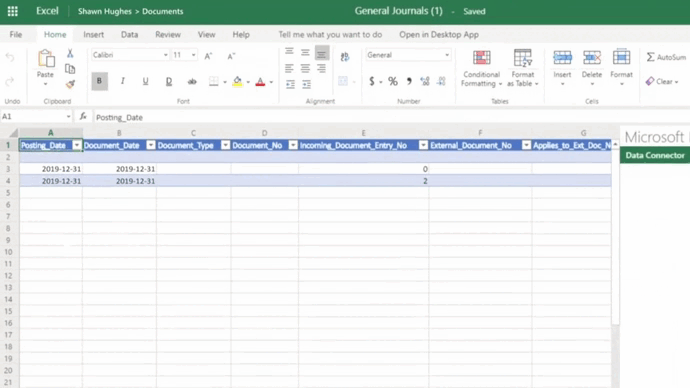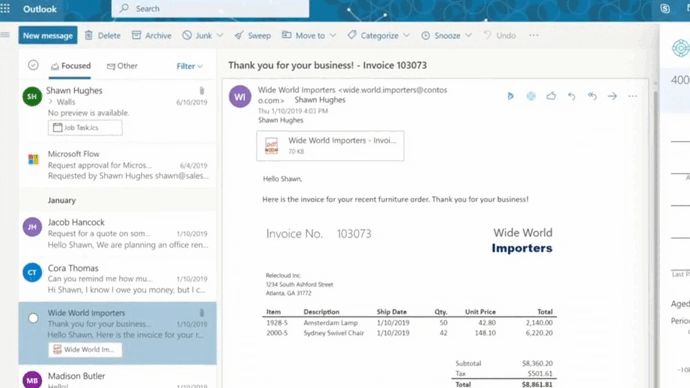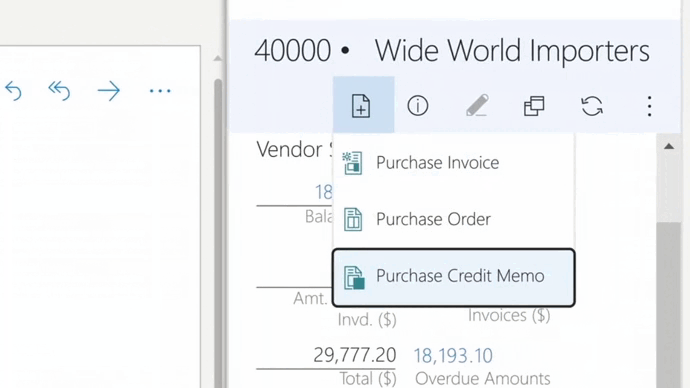
Types of ERP software by deployment model
One of the most common ways to categorize types of ERP software is by deployment. These models determine how the system is hosted, managed, and maintained.
On-premise ERP systems
On-premise ERP is installed on your own servers and managed by your internal IT team.
Benefits:
- Full control and customization.
- Strong data security with information stored locally.
- No recurring subscription fees.
Drawbacks:
- High upfront investment in hardware and software.
- Ongoing IT maintenance and upgrade responsibilities.
- Less flexibility for remote or distributed teams.
Best for: large organizations with dedicated IT staff, strict compliance requirements, or complex customization needs.

Cloud ERP systems
Cloud-based ERP runs on vendor-managed servers and is accessed via the internet on a subscription model.
Benefits:
- Lower upfront cost.
- Automatic updates and upgrades.
- High scalability and flexibility.
- Accessible anywhere, on any device.
Drawbacks:
- Dependence on internet connectivity.
- Ongoing subscription fees.
- Vendor-managed security (though top providers invest heavily in this).
Best for: growing businesses that want cost-effective, scalable solutions.
Hybrid ERP systems
Hybrid ERP combines on-premise and cloud solutions, offering flexibility for businesses with specific needs.
Benefits:
- Retain sensitive data on-premise while using cloud apps for scalability.
- Gradual migration path for businesses transitioning from legacy systems.
- Suitable for organizations with multiple global locations.
Drawbacks:
- More complex to implement and manage.
- Higher long-term costs compared to pure cloud solutions.
Best for: companies in highly regulated industries or those wanting to modernize without a full migration.
Web-based ERP systems
Web-based ERP runs entirely through a browser without requiring heavy local installation.
Benefits:
- Lightweight and easy to deploy.
- Accessible across devices.
- Lower IT overhead.
Best for: small to mid-sized businesses or teams that need quick, accessible solutions.
Types of ERP software by functionality
Beyond deployment, ERP software types can also be defined by the business functions they serve.
Finance ERP systems
Focused on accounting, reporting, and compliance. Ideal for businesses that need strong financial management capabilities.
Manufacturing ERP systems
Tailored to production scheduling, material requirements planning (MRP), and quality control. A must-have for manufacturers.
Supply chain ERP systems
Provide visibility and automation across procurement, logistics, inventory, and vendor management.
How much can you save?
Download your free ROI Excel calculator to discover how much savings you can make with Business Central today.

HR-focused ERP systems
Specialize in employee data management, payroll, recruitment, and performance tracking.
CRM-integrated ERP systems
Combine ERP with customer relationship management, aligning finance, operations, and customer data for better decision-making.
Industry-specific ERP solutions
Healthcare, construction, retail, and government often rely on ERP tailored to their unique regulatory and operational needs.

Types of ERP modules every business should know
ERP software is modular. Businesses can start with core modules and expand as they grow. Key ERP modules include:
- Finance & accounting – General ledger, accounts payable/receivable, compliance.
- Procurement – Vendor management, purchase orders, spend control.
- Inventory management – Track stock levels, warehouses, and replenishment.
- Supply chain management – From demand planning to logistics optimization.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) – Manage customer interactions and sales pipelines.
- Human Capital Management (HCM) – Payroll, HR, workforce planning.
- Project management – Resource allocation, cost tracking, billing.
- Business intelligence & analytics – Real-time reporting and forecasting.
These modules form the building blocks of a complete ERP strategy.
Popular examples of ERP software
To better understand the different ERP systems, here are some leading examples:
- Microsoft Dynamics 365– A modular, cloud-first ERP platform that integrates finance, supply chain, sales, HR, and CRM. It’s AI-enabled, highly scalable, and a strong choice for Canadian businesses when implemented by partners like Gestisoft.
- SAP S/4HANA– Powerful ERP suite with strong analytics and enterprise-grade scalability.
- Oracle NetSuite– Cloud ERP known for financial management and global reach.
- Infor CloudSuite– Industry-specific ERP with built-in AI.
- Odoo – Open-source ERP with extensive customization.
- Acumatica – Cloud ERP for SMBs with strong integration options.

How to choose the right type of ERP software for your business?
Selecting the right ERP requires a structured approach:
- Identify business needs – Define what problems you need ERP to solve.
- Budget considerations – Balance upfront vs. long-term costs.
- Scalability – Ensure the system can grow with your company.
- Compliance requirements – Consider regulatory needs in your industry.
- Vendor support – Look for strong local implementation partners like Gestisoft.
Tip: Cloud ERPworks best for most growing businesses, but industries with strict compliance (healthcare, defense, government) may require hybrid or on-premise deployments.
Future of ERP software types
The next generation of ERP is being shaped by:
- AI & automation – Smarter forecasting, predictive analytics, and process automation.
- Industry 4.0 integration – IoT and advanced manufacturing integration.
- Cloud dominance – Most businesses moving away from legacy systems.
- Personalization – ERP platforms adapting to specific industries and even individual organizations.
These trends make ERP more strategic than ever.
Book a free consultation with our ERP experts today
Contact us to learn more about the type of ERP software that we have - Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central.
 Free discovery call
Free discovery call
Why Microsoft Dynamics 365 is the most complete ERP solution?
Among all types of ERP software, Microsoft Dynamics 365 stands out for its flexibility. It offers:
- Unified finance, supply chain, HR, and CRM modules.
- Native AI and real-time analytics.
- Seamless integration with Microsoft 365 tools (Excel, Outlook, Teams).
- Industry-specific extensions through partners like Gestisoft.
With Gestisoft as your Microsoft Dynamics 365 partner, you gain expert guidance, localized support, and a proven track record in helping businesses transform through ERP.
-
On-premise, cloud, hybrid, web-based, and industry-specific ERP.
Conclusion
Understanding the different types of ERP software is essential for making the right technology investment. From deployment models (cloud, on-premise, hybrid) to functional modules (finance, supply chain, HR, CRM) and industry-specific solutions, ERP provides the foundation for growth and efficiency.
The future of ERP is cloud-first, AI-powered, and increasingly industry-tailored. Among available solutions, Microsoft Dynamics 365 offers one of the most complete and flexible platforms—and with Gestisoft as your partner, you gain a trusted guide to implement, customize, and scale your ERP journey successfully. Contact us for a free consultation and to discover how we can help you.
Liked what you just read? Sharing is caring.

September 29, 2025 by Kooldeep Sahye by Kooldeep Sahye Marketing Specialist
Fuelled by a passion for everything that has to do with search engine optimization, keywords and optimization of content. And an avid copywriter who thrives on storytelling and impactful content.
